Some of the links in this article are "affiliate links", a link with a special tracking code. This means if you click on an affiliate link and purchase the item, we will receive an affiliate commission.
The price of the item is the same whether it is an affiliate link or not. Regardless, we only recommend products or services we believe will add value to our readers.
By using the affiliate links, you are helping support our Website, and we genuinely appreciate your support.
When applying for jobs, the resume is one of the most critical components of your application. It serves as your first impression, showcasing your skills, experiences, and qualifications. However, there isn’t just one “right” way to format a resume. Depending on your work history, skills, and the position you’re applying for, there are several types of resumes you can choose from. In this article, we’ll explore the most common resume formats and help you determine which one suits your career goals best.
1. Chronological Resume
Best for: Job seekers with a strong, consistent work history in a specific industry.
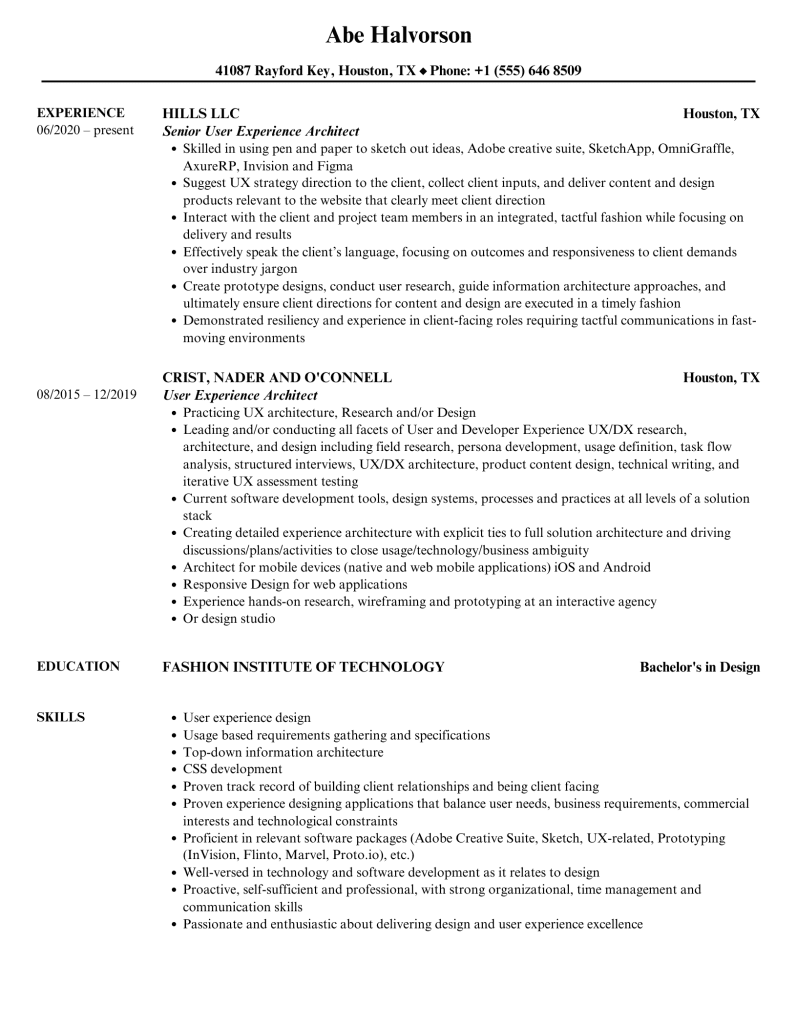
A chronological resume is the most common and traditional resume format. This type of resume focuses on your work history, listing jobs in reverse chronological order (starting with the most recent). It highlights your career progression, making it an ideal choice for those with a steady job history in the same field.
Key Features:
- Work Experience: Listed in reverse chronological order.
- Emphasis on Career Progression: Highlights job growth and accomplishments over time.
- Education: Usually placed after work experience.
Pros:
- Easy to read and familiar to most employers.
- Showcases career growth and longevity.
- Great for applicants with consistent employment in a particular field.
Cons:
- Can highlight employment gaps or job-hopping.
- Not ideal for those with limited experience or frequent career changes.
2. Functional Resume
Best for: Job seekers with gaps in employment, changing careers, or those with diverse work experiences.
A functional resume focuses on your skills and qualifications rather than your chronological work history. This type of resume is especially helpful if you’re changing careers or have gaps in your employment history. It allows you to showcase your abilities without drawing attention to your lack of experience in a particular industry or role.
Key Features:
- Skills-Based Sections: Organizes experience under skill categories (e.g., Leadership, Technical Skills, Communication).
- Less Focus on Work History: Job experience is minimized or briefly listed.
- Emphasis on Accomplishments: Highlights transferable skills and achievements.
Pros:
- Useful for career changers or those with a non-traditional career path.
- De-emphasizes gaps or lack of experience in a specific role.
Cons:
- Can be challenging for hiring managers to understand the full scope of your career.
- Might be perceived as an attempt to hide work history gaps.
3. Combination (Hybrid) Resume
Best for: Applicants with a mix of skills and experience or those with a diverse background.
The combination resume merges the best elements of both the chronological and functional resumes. It starts by showcasing your skills and qualifications, followed by a detailed work history in reverse chronological order. This format is perfect for job seekers who want to emphasize their skills while still demonstrating their professional journey.
Key Features:
- Skills and Experience: Focuses on skills and accomplishments first.
- Detailed Work History: Provides a chronological list of previous roles.
- Flexible: Works well for both experienced professionals and career changers.
Pros:
- Balances showcasing skills and detailing work history.
- Ideal for those with diverse skills or seeking to transition between fields.
Cons:
- Can become lengthy if not carefully tailored.
- Requires careful structuring to avoid overwhelming the reader.
4. Targeted Resume
Best for: Applicants applying for a specific job, where customization is key.
A targeted resume is tailored specifically to a particular job opening. It customizes the content to match the job description, using keywords and phrases from the job listing to highlight the most relevant skills and experiences. This approach requires you to adjust your resume for each job you apply to but increases your chances of passing through applicant tracking systems (ATS) and catching the attention of hiring managers.
Key Features:
- Customized Content: Tailors your experience, skills, and qualifications to the job posting.
- Increased Use of Keywords: Includes keywords from the job description to optimize your resume for ATS.
- Emphasis on Relevance: Only includes experiences and skills relevant to the job at hand.
Pros:
- Maximizes chances of getting noticed by ATS and hiring managers.
- Highlights the most relevant experiences for the specific job.
Cons:
- Time-consuming to create different resumes for each job application.
- Requires careful attention to detail to ensure it matches the job description.
5. Curriculum Vitae (CV)
Best for: Academia, research, or other fields that require an in-depth look at your qualifications.
A Curriculum Vitae (CV) is a more detailed version of a resume and is typically used in academic, research, or international job markets. Unlike a resume, which is usually one to two pages, a CV can be multiple pages and includes a comprehensive overview of your academic background, research, publications, certifications, teaching experience, and more.
Key Features:
- Length: Much longer than a standard resume, often spanning multiple pages.
- Detailed Sections: Includes sections for education, research, publications, conferences, honors, and more.
- Focus on Academic and Professional Achievements: Highlights scholarly accomplishments and professional contributions.
Pros:
- Ideal for those in academia or research.
- Offers a comprehensive view of your career and achievements.
Cons:
- Not suitable for non-academic fields.
- Can be too detailed for some employers.
6. Creative Resume
Best for: Creative professionals, such as graphic designers, artists, writers, and marketers.
A creative resume breaks the mold of traditional resume formats and is an excellent choice for professionals in creative industries. This type of resume often uses visuals, infographics, and unique layouts to showcase creativity and stand out from the crowd. While a creative resume can be visually appealing, it should still be clear and readable.
Key Features:
- Visual Design: Incorporates graphics, colors, and creative layouts.
- Showcases Creativity: Allows you to express your personal style and artistic abilities.
- Portfolio Integration: Often includes links to a portfolio or examples of work.
Pros:
- Perfect for creative fields where design and innovation are key.
- Helps make a strong visual impact.
Cons:
- May not be suitable for traditional or corporate industries.
- Can be difficult for ATS to process.
Conclusion
Choosing the right type of resume depends on your career path, work history, and the industry you’re targeting. Whether you opt for the traditional chronological format, the skills-focused functional resume, or a creative resume, tailoring it to your specific situation will help you stand out to potential employers. Make sure your resume highlights your strengths and presents you as the best candidate for the job.
By understanding the different types of resumes, you can select the one that best showcases your qualifications and maximizes your chances of landing the job of your dreams.